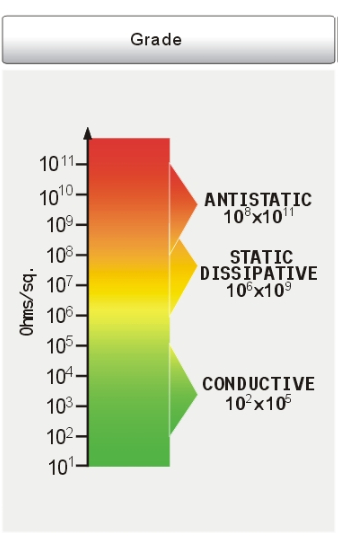
ESDmaterials are generally subdivided into categories with related properties:Anti-Static, Conductive, and Static Dissipative
|
Ohms Per Square |
Material |
Description |
|
> 1012 |
Insulative |
Insulators and Base Polymers. Not an ESD material |
|
109 to 1012 |
Anti-Static |
Initial charges are suppressed |
|
106 to 109 |
Dissipative |
No or low initial charge. Prevents discharge to or from human contact |
|
103 to 106 |
Conductive |
No initial charge. Provides path for charge to bleed-off |
|
1 to 103 |
Shielding |
|
|
10-3 to 1 |
Carbon |
Carbon powders and fiber |
|
< 10-3 |
Metals |
Insulative
Insulativematerials prevent or limit the flow of electrons across their surface orthrough their volume. Insulative materials have a high electrical resistanceand are difficult to ground, thus are not ESD materials. Static charges remainin place on these materials for a very long time.
Anti-Static
Anti-staticmaterials are generally referred to as any material which inhibitstriboelectric charging. This kind of charging is the buildup of an electriccharge by the rubbing or contact with another material. One type of anti-staticpackaging material is commonly referred to as Pink Poly. It is a clearpink (hot pink) polyethylene that is available as a film for bags, bubble pack,or foam.
Dissipative
Dissipativematerials allow the charges to flow to ground more slowly in a more controlledmanner than with conductive materials.
Conductive
Conductivematerials have a low electrical resistance, thus electrons flow easily acrossthe surface or through these materials. Charges go to ground or to anotherconductive object that the material contacts.
